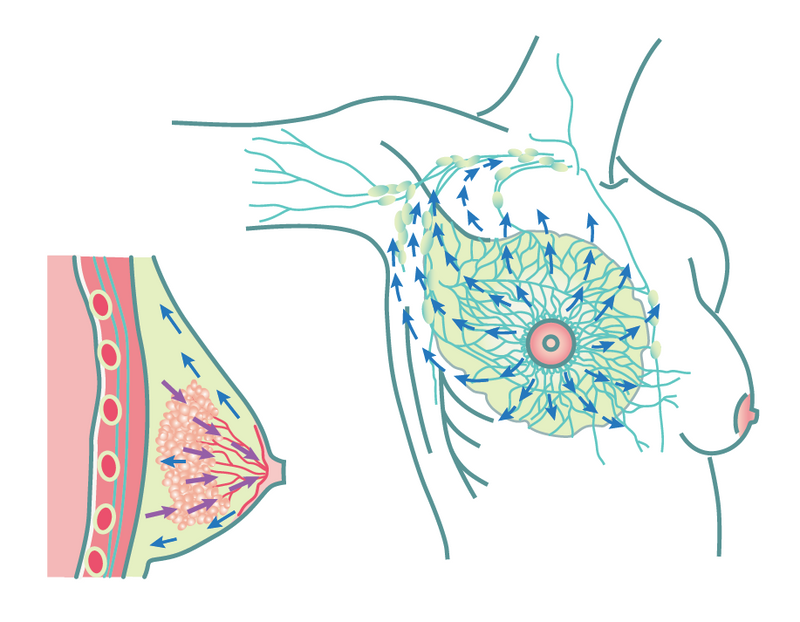
COMT methylation protective against undesirable estrogen metabolites https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11606384/
Magnesium, PMS, mastalgia https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6684167/
Magnesium: physiology and pharmacology
https://www.bjanaesthesia.org/article/S0007-0912(17)38397-6/pdf
Magnesium glycinate and myometrial relaxation https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7071389/pdf/nutrients-12-00573.pdf
Article on estrogen metabolism, COMT, and magnesium by a physician / biochemist https://www.drlaurendeville.com/articles/estrogen-detoxification/
Calcium D-glucarate monograph - https://altmedrev.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/v7-4-336.pdf
Calcium D-glucarate as a beta-glucuronidase inhibitor https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18772850/
Article on Calcium D-glucarate and estrogen metabolism, NMD journal https://ndnr.com/endocrinology/estrogen-dominance-in-women/
Article on Calcium D-glucarate from a functional medicine physician / biochemist https://drbrighten.com/benefits-of-calcium-d-glucarate/
Composition and physiological activities of Borage seed oil - https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25312125/
GLA and cyclic mastalgia https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18296341/
GLA, eicosanoids, and inflammation https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4975646/pdf/nihms781789.pdf
Borage oil and inflammatory gene expression https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2708836/pdf/zbc15400.pdf
GLA and PMS-associated inflammation / dysmenorrhea
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18296341/
Black seed oil for cyclic mastalgia https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6820470/pdf/2093-6966-v22-n03-131.pdf
Black seed oil as an anti-inflammatory agent https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33559935/
Nigella sativa: monograph https://www.phytojournal.com/archives/2015/vol4issue4/PartB/4-3-79.pdf
Black seed oil for breast health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7460502/pdf/medicines-07-00047.pdf and
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26964971/ and
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6921197/pdf/main.pdf
See the extensive clinical monograph on Phytolacca in Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy, 2nd. Ed., Simon Mills & Kerry Bone. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2013. Pp. 795-798.
Phytolacca in King’s American Dispensatory, the standard Eclectic medical publication of 1898 https://www.henriettes-herb.com/eclectic/kings/phytolacca.html
Ruth Trickey (with practitioners from the Melbourne Holistic Health Group), respected midwife and herbalist, mentions the use of Poke for mastalgia in her classic Women, Hormones & the Menstrual Cycle, 3rd Ed., Trickey Enterprises (Victoria) Pty, Limited; 2011.
Bioactive triterpene saponins from Phytolacca americana https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33002830/
Dr. Aviva Romm mentions topical Phytolacca for benign breast disease in Botanical Medicine for Women’s Health (p. 595), Churchill Livingstone; 2nd Ed.; 2017.
Effective medicinal plants for cyclic mastalgia, a review https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6820470/
Topical application of St. John’s Wort https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24214835/
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Hypericum oil https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24993886/
Cell-growth regulating effects of the oil-soluble constituents https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33379141/
See the extensive clinical monograph on Hypericum in Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy, 2nd. Ed., Simon Mills & Kerry Bone. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2013. Pp. 826-860.
Parsay S, Olfati F, Nahidi S. Therapeutic effects of vitamin E on cyclic mastalgia. Breast Journal. 2009;15:510–4. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19614907
American Herbal Pharmacopoeia (AHP) monograph on Trifolium http://pharmaguri.co.il/_Uploads/dbsAttachedFiles/AHPTrifoliumMonograph.pdf
Review – pharmacology of the main isoflavonoid in Trifolium, Biochanin A https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6639423/pdf/fphar-10-00793.pdf
Trifolium’s potential as a complementary therapy in breast cancer (apoptotic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7455927/
Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of Red Clover 2021 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34392659/
Isoflavones (Trifolium constituent) and mastalgia, clinical trial https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14965665/
Clinical actions of Red Clover https://restorativemedicine.org/library/monographs/red-clover/
Anti-inflammatory activity of Andrographis and andrographolide https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25888070/
Anti-inflammatory diterpenoid lactones in Andrographis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31357563/
Andrographis review: ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4408759/pdf/TSWJ2014-274905.pdf
See the extensive clinical monograph on Andrographis in Principles and Practice of Phytotherapy, 2nd. Ed., Simon Mills & Kerry Bone. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier; 2013. Pp. 360-372.
See Discover Andrographis by Alexander Panossian, Ph.D. Detailed monograph/book. https://www.academia.edu/40480219/DISCOVER_ANDROGRAPHIS